information
INFORMATIONHOTLINE
+86-0531-85667509T e l:+86-0531-85667509
F a x:86-0531-85667508
E-mai:warwickpump@gmail.com
Technology article
Materials and Temperatures of the high temperature molten sa
The temperature is the starting point for selecting the materials of construction used for the pump. Operating temperature ranges for molten salt start just above their melting point, about 238-deg C (435-deg F), and can run as high as 1200-deg C (2192-deg F).
The salt chemistry must also be considered, because it is absolutely necessary to understand the temperature at which the molten salt will decompose. Many salts will form hazardous gases and may become more aggressively corrosive at the liquid/atmospheric line of the pump or attack the welds.
Because temperature weakens the strength of all materials, the correct materials and designs are reviewed together. The materials used can often compensate for inherently weaker designs being dictated by space limitations or the type of pump used. The reverse is also true, when the design will compensate for weaknesses in the materials due to high temperatures. Understanding this relationship is crucial to selecting the right pump for a given application.
The length of the pump and the operating temperature of the molten salt greatly affect the basic design and material selection of the pump. Selecting a material that falls into the marginal range, or even at the extreme high end of the temperature range, can be very dangerous. The risk of a weak structure that will cause a maintenance nightmare must be avoided at all cost. Purchasing the wrong combination of materials and equipment design will create a catastrophic failure of the molten salt system.
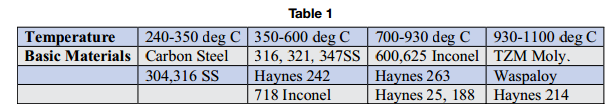
High temperatures and basic materials can be divided into four major categories, as shown in Table 1. This is only a guideline and not respective of a specific application.
Before selecting a material, the correlation between the type of salt, temperature range or ranges, velocities within the pump volute and discharge, thermal expansion of the pump shaft, column and discharge assemblies, and mounting arrangement of the pump must be evaluated. Each of these factors influence the type of materials used to best meet the application.
The type of salts used in molten salt applications varies widely, from simple compound salts like sodium nitrates and potassium nitrates to blended complexes, such as fluoridebased salts like FLiNaK. Understanding their melting points, decomposition temperatures, corrosion characteristics, need for agitation, fluid density at different temperatures and freezing points all help in selecting the proper materials.
Temperature ranges that vary can cause distortion and binding in the rotating elements of the pump. For this reason, calculations of each range must be performed to determine the thermal expansion effects on the pump’s rotating assembly and stationary components to ensure the proper materials are used in case these temperature changes occur.
The thermal expansion of the rotating assembly and stationary components of the pump must be matched to prevent distortion and binding of the rotating assembly. Materials of each that have similar thermal expansion rates will simplify the pump design. Both lateral and diametrical dimensions must be calculated to ensure that the pump rotates freely and there is no distortion in the column and discharge assemblies.
Fluid velocities and temperature can cause high erosion of impeller vane tips, volute cut waters and discharge elbows. Fluid relative velocity should be kept in a range of 10-fps to 12-fps. Erosion/corrosion damage is usually proportional to the tip-speed to the 6th power – the higher the tip speed, the more severe the erosion/corrosion damage becomes.
The mounting plate serves two major design functions. First, the strength of the mounting plate plays a critical role in pump stability and performance. It supports the pump and motor and keeps everything in alignment. The movement that a pump generates can damage the discharge piping if the mounting plate flexes.
Second, vibration levels can be very high if the mounting plate is weakened by the heat. Both axial and radial vibration can cause severe damage to the pump if the mounting plate is weak. The mounting plate normally has an insulation barrier that prevents the high temperature of the salt from deforming and weakening it. Again, selecting the proper material is critical.